Support two watchdog controls of the board. If the watchdog begins and reaches the pre-set time, it will access the CPU’s RESET signal to reset the system.
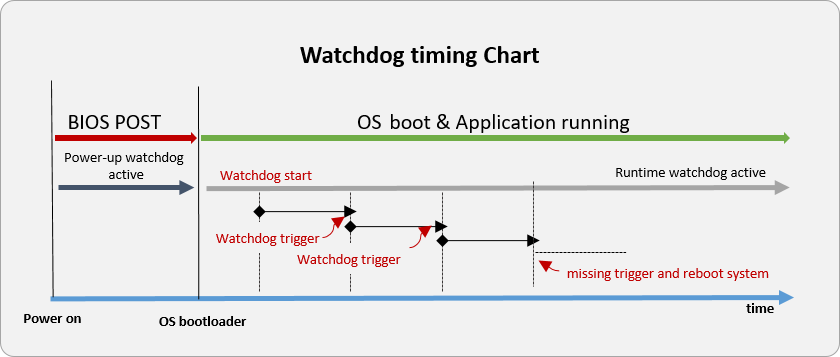
Run-Time Watchdog: used in the OS to monitor the process or the application. BIOS also provides the capability to enable, disable and setup timeout value on BIOS Menu. If enable run-time watchdog on BIOS menu, please make a trigger to extend the timeout or system reboot.
Note: timeout value will continuously keep until run-time watchdog is disabled on BIOS Menu or using SEMA functions to stop it.
Power-up Watchdog: used to supervise the boot process between system power-on to the operating system loading. When BIOS POST can be successfully booted, BIOS will clear power-up watchdog and go to OS bootloader. BIOS also provides the capability to enable, disable and setup timeout value on BIOS Menu.
Note: Reboot system is a must after using SEMA function to enable power-up watchdog.
sysfs Interfaces
For Run-time Watchdog:
To start/update the run-time watchdog with timeout out value, use the following format:
wdogtest –timeout=<time in seconds>
The example below sets the run-time watchdog timeout value as 20 seconds.
wdogtest –timeout=20
To stop the run-time watchdog ( Timeout value will be set to ‘0’. Please set timeout again)
echo "V" > /dev/watchdog0
To trigger / ping the run-time watchdog
wdogtest –ping
To get the information about the run-time watchdog state
cat /sys/class/watchdog/watchdog0/state
- To get the current run-time watchdog timeout value ( timeout value is not the elapsed time. it is your initial timeout)
cat /sys/class/watchdog/watchdog0/timeout
- To get minimum/maximum run-time watchdog timeout value
/sys/bus/platform/devices/adl-bmc-wdt/Capabilities/wdt_min_timeout
/sys/bus/platform/devices/adl-bmc-wdt/Capabilities/wdt_max_timeout
For Power-up Watchdog
To start / update the power-up watchdog timer value:
echo <time in seconds> /sys/bus/platform/devices/adl-bmc-wdt/Capabilities/PwrUpWDog
The example below sets the power-up watchdog timer timeout value as 1000 seconds:
echo 1000 > /sys/bus/platform/devices/adl-bmc-wdt/Capabilities/PwrUpWDogTo get the power-up watchdog timer value
cat /sys/bus/platform/devices/adl-bmc-wdt/Capabilities/PwrUpWDog
To stop the power-up watchdog timer
echo 0 > /sys/bus/platform/devices/adl-bmc-wdt/Capabilities/PwrUpWDog
SEMA EAPI (Both Windows & Linux supported)
Get the capabilities of run-time watchdog
uint32_t EApiWDogGetCap( |
Parameters:
uint32_t *pMaxDelay:
Pointer to a buffer that receives maximum supported initial delay time of the watchdog timer in milliseconds.
uint32_t *pMaxEventTimeout:
Pointer to a buffer that receives maximum supported event timeout of the watchdog timer in milliseconds.
uint32_t* Resetvalue:
Pointer to a buffer that receives maximum supported event timeout of the watchdog timer in milliseconds.
Start to run-time watchdog timer. To reset timer value, timer must be stopped by using EApiWDogStop() and then EApiWDogStart() be called again with new values.
uint32_t EApiWDogStart( |
Parameters:
uint32_t delay:
Initial delay for the watchdog timer in milliseconds. (currently not supported by SEMA EAPI, set it as 0)
uint32_t EventTimeout:
Initial delay for the watchdog timer in milliseconds. (currently not supported by SEMA EAPI, set it as 0)
uint32_t ResetTime:
Watchdog timeout interval in milliseconds to trigger a reset.
Reset the run-time watchdog timer
uint32_t EApiWDogTrigger() |
Stop the operation of the run-time watchdog timer
uint32_t EApiWDogStop() |
Enable the operation of the power-up watchdog timer
uint32_t EApiPwrUpWDogStart( uint32_t ResetTime) |
Parameters:
uint32_t ResetTime:
Watchdog timeout interval in milliseconds to trigger a reset.
Disable the operation of the power-up watchdog timer (disable)
uint32_t EApiPwrUpWDogStop() |